Advanced layouts with flexbox
07 Jun 2015Flexbox
The defining aspect of the flexbox is the ability to alter its items, width and/or height to best fill the available space on any display device. A flex container expands its items to fill the available free space, or shrinks them to prevent overflow.
Problems with float layout
- Difficulty with containement - If our site has some unpredictable content then it becomes difficult to maintain the layout with floats. Also it becomes tedious maintaining this.
- Source order dependence - The layout is HTMl source dependent, so it becomes difficult to alter the layout for different media queries for responsive sites.
- Equal Height Columns issues - If we have 2-3 columns with different content in them and we need them to be of equal height irrespective of the content in it, then it becomes very difficult.
- Content Centering - Using floats its very cumbersome to make the content of div to align in center both vertically and horizontally.
How flexbox cures these issues
- Makes flex items grow to fill available space for or shring to avaoid overflow. By this it resolves the issue of unknown content overflowing also aligns layouts to adhere to the expectations of the themer.
- It gives flex items a proportional dimensions
- Flex items inside the flex containers can be layed out in any direction, so this solves our issue with content order in different media queries. It makes the visual content order to be independent of the HTML markup order thereby helping in the responsive theming of sites.
Flexbox properties
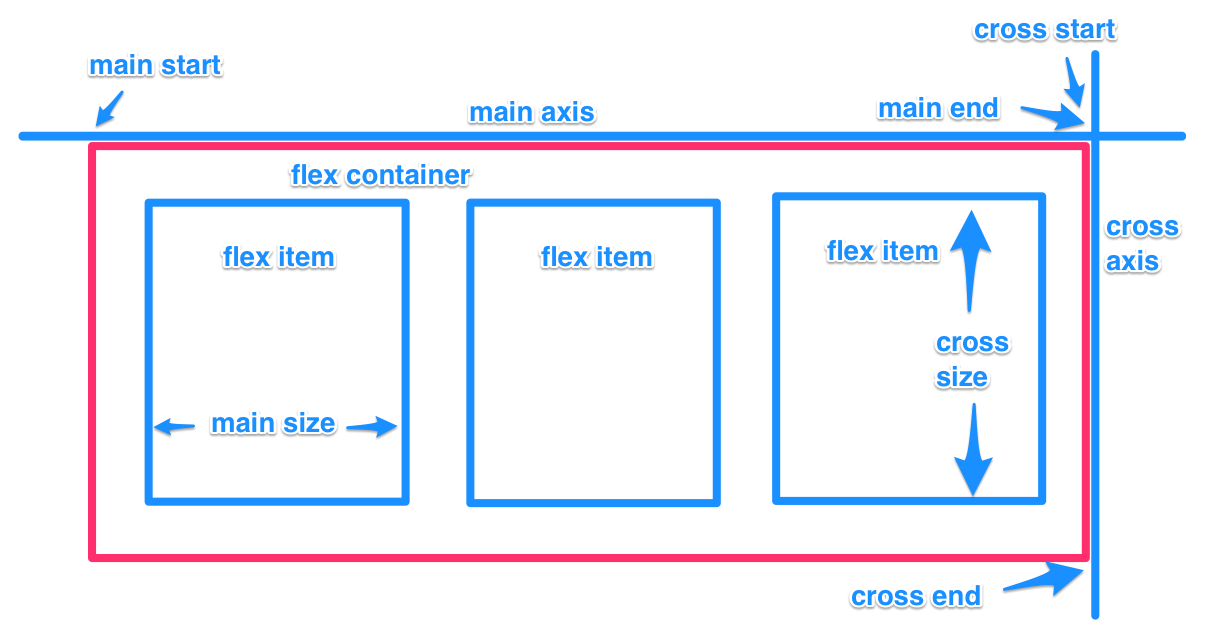
- main axis, main dimension - The main axis of a flex container is the primary axis along which flex items are laid out. It extends in the main dimension.
- main-start, main-end - The flex items are placed within the container starting on the main-start side and going toward the main-end side.
- main size,main size property - A flex item’s width or height, whichever is in the main dimension, is the item’s main size. The flex item’s main size property is either the width or height property, whichever is in the main dimension.
- cross axis, cross dimension - The axis perpendicular to the main axis is called the cross axis. It extends in the cross dimension.
- cross-start,cross-end - Flex lines are filled with items and placed into the container starting on the cross-start side of the flex container and going toward the cross-end side.
- cross size,cross size property - The width or height of a flex item, whichever is in the cross dimension, is the item’s cross size. The cross size property is whichever of width or height that is in the cross dimension.
Flex Container properties
Flex items properties
Flexbox Mixins
This is a set of mixins for those who want to mess around with flexbox using the native support of current browsers. For full support table
check: http://caniuse.com/flexbox
Basically this will use:
- Fallback, old syntax (IE10, mobile webkit browsers - no wrapping)
- Final standards syntax (FF, Safari, Chrome, IE11, Opera)
This was inspired by:
With help from:
- http://w3.org/tr/css3-flexbox/
- http://the-echoplex.net/flexyboxes/
- http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ie/hh772069(v=vs.85).aspx
- http://css-tricks.com/using-flexbox/
- http://dev.opera.com/articles/view/advanced-cross-browser-flexbox/
- https://developer.mozilla.org/en-us/docs/web/guide/css/flexible_boxes
Flexbox Containers
The 'flex' value causes an element to generate a block-level flexcontainer box.
The 'inline-flex' value causes an element to generate a inline-level flex container box.
display: flex | inline-flex http://w3.org/tr/css3-flexbox/#flex-containers
@mixin flexbox {
display: -webkit-box;
display: -webkit-flex;
display: -moz-flex;
display: -ms-flexbox;
display: flex;
}
//Using this mixin
%flexbox { @include flexbox; }@mixin inline-flex {
display: -webkit-inline-box;
display: -webkit-inline-flex;
display: -moz-inline-flex;
display: -ms-inline-flexbox;
display: inline-flex;
}
%inline-flex { @include inline-flex; }Flexbox Direction
The 'flex-direction' property specifies how flex items are placed in the flex container, by setting the direction of the flex container's main axis. This determines the direction that flex items are laid out in.
Values: row | row-reverse | column | column-reverse http://w3.org/tr/css3-flexbox/#flex-direction-property
@mixin flex-direction($value: row) {
@if $value == row-reverse {
-webkit-box-direction: reverse;
-webkit-box-orient: horizontal;
} @else if $value == column {
-webkit-box-direction: normal;
-webkit-box-orient: vertical;
} @else if $value == column-reverse {
-webkit-box-direction: reverse;
-webkit-box-orient: vertical;
} @else {
-webkit-box-direction: normal;
-webkit-box-orient: horizontal;
}
-webkit-flex-direction: $value;
-moz-flex-direction: $value;
-ms-flex-direction: $value;
flex-direction: $value;
}
// Shorter version:
@mixin flex-dir($args...) { @include flex-direction($args...); }Flexbox Wrap
The 'flex-wrap' property controls whether the flex container is single-line or multi-line, and the direction of the cross-axis, which determines the direction new lines are stacked in.
Values: nowrap | wrap | wrap-reverse Default: nowrap
http://w3.org/tr/css3-flexbox/#flex-wrap-property
@mixin flex-wrap($value: nowrap) {
// No Webkit Box fallback.
-webkit-flex-wrap: $value;
-moz-flex-wrap: $value;
@if $value == nowrap {
-ms-flex-wrap: none;
} @else {
-ms-flex-wrap: $value;
}
flex-wrap: $value;
}Flexbox Flow (shorthand)
The 'flex-flow' property is a shorthand for setting the 'flex-direction' and 'flex-wrap' properties, which together define the flex container's main and cross axes.
Values:
http://w3.org/tr/css3-flexbox/#flex-flow-property
@mixin flex-flow($values: (row nowrap)) {
// No Webkit Box fallback.
-webkit-flex-flow: $values;
-moz-flex-flow: $values;
-ms-flex-flow: $values;
flex-flow: $values;
}Flexbox Order
The 'order' property controls the order in which flex items appear within their flex container, by assigning them to ordinal groups.
Default: 0
http://w3.org/tr/css3-flexbox/#order-property
@mixin order($int: 0) {
-webkit-box-ordinal-group: $int + 1;
-webkit-order: $int;
-moz-order: $int;
-ms-flex-order: $int;
order: $int;
}Flexbox Grow
The 'flex-grow' property sets the flex grow factor. Negative numbers are invalid.
Default: 0
http://w3.org/tr/css3-flexbox/#flex-grow-property
@mixin flex-grow($int: 0) {
-webkit-box-flex: $int;
-webkit-flex-grow: $int;
-moz-flex-grow: $int;
-ms-flex-positive: $int;
flex-grow: $int;
}Flexbox Shrink
The 'flex-shrink' property sets the flex shrink factor. Negative numbers are invalid.
Default: 1
http://w3.org/tr/css3-flexbox/#flex-shrink-property
@mixin flex-shrink($int: 1) {
-webkit-flex-shrink: $int;
-moz-flex-shrink: $int;
-ms-flex-negative: $int;
flex-shrink: $int;
}Flexbox Basis
The 'flex-basis' property sets the flex basis. Negative lengths are invalid.
Values: Like "width" Default: auto
http://www.w3.org/TR/css3-flexbox/#flex-basis-property
@mixin flex-basis($value: auto) {
-webkit-flex-basis: $value;
-moz-flex-basis: $value;
-ms-flex-preferred-size: $value;
flex-basis: $value;
}Flexbox "Flex" (shorthand)
The 'flex' property specifies the components of a flexible length: the flex grow factor and flex shrink factor, and the flex basis. When an element is a flex item, 'flex' is consulted instead of the main size property to determine the main size of the element. If an element is not a flex item, 'flex' has no effect.
Values: none |
Default: See individual properties (1 1 0).
http://w3.org/tr/css3-flexbox/#flex-property
@mixin flex($fg: 1, $fs: null, $fb: null) {
// Set a variable to be used by box-flex properties
$fg-boxflex: $fg;
// Box-Flex only supports a flex-grow value so lets grab the
// first item in the list and just return that.
@if type-of($fg) == 'list' {
$fg-boxflex: nth($fg, 1);
}
-webkit-box-flex: $fg-boxflex;
-webkit-flex: $fg $fs $fb;
-moz-box-flex: $fg-boxflex;
-moz-flex: $fg $fs $fb;
-ms-flex: $fg $fs $fb;
flex: $fg $fs $fb;
}Flexbox Justify Content
The 'justify-content' property aligns flex items along the main axis of the current line of the flex container. This is done after any flexible lengths and any auto margins have been resolved. Typically it helps distribute extra free space leftover when either all the flex items on a line are inflexible, or are flexible but have reached their maximum size. It also exerts some control over the alignment of items when they overflow the line.
Note: 'space-*' values not supported in older syntaxes.
Values: flex-start | flex-end | center | space-between | space-around Default: flex-start
http://w3.org/tr/css3-flexbox/#justify-content-property
@mixin justify-content($value: flex-start) {
@if $value == flex-start {
-webkit-box-pack: start;
-ms-flex-pack: start;
} @else if $value == flex-end {
-webkit-box-pack: end;
-ms-flex-pack: end;
} @else if $value == space-between {
-webkit-box-pack: justify;
-ms-flex-pack: justify;
} @else if $value == space-around {
-ms-flex-pack: distribute;
} @else {
-webkit-box-pack: $value;
-ms-flex-pack: $value;
}
-webkit-justify-content: $value;
-moz-justify-content: $value;
justify-content: $value;
}
// Shorter version:
@mixin flex-just($args...) { @include justify-content($args...); }Flexbox Align Items
Flex items can be aligned in the cross axis of the current line of the flex container, similar to 'justify-content' but in the perpendicular direction. 'align-items' sets the default alignment for all of the flex container's items, including anonymous flex items. 'align-self' allows this default alignment to be overridden for individual flex items. (For anonymous flex items, 'align-self' always matches the value of 'align-items' on their associated flex container.)
Values: flex-start | flex-end | center | baseline | stretch Default: stretch
http://w3.org/tr/css3-flexbox/#align-items-property
@mixin align-items($value: stretch) {
@if $value == flex-start {
-webkit-box-align: start;
-ms-flex-align: start;
} @else if $value == flex-end {
-webkit-box-align: end;
-ms-flex-align: end;
} @else {
-webkit-box-align: $value;
-ms-flex-align: $value;
}
-webkit-align-items: $value;
-moz-align-items: $value;
align-items: $value;
}Flexbox Align Self
Values: auto | flex-start | flex-end | center | baseline | stretch Default: auto
@mixin align-self($value: auto) {
// No Webkit Box Fallback.
-webkit-align-self: $value;
-moz-align-self: $value;
@if $value == flex-start {
-ms-flex-item-align: start;
} @else if $value == flex-end {
-ms-flex-item-align: end;
} @else {
-ms-flex-item-align: $value;
}
align-self: $value;
}Flexbox Align Content
The 'align-content' property aligns a flex container's lines within the flex container when there is extra space in the cross-axis, similar to how 'justify-content' aligns individual items within the main-axis. Note, this property has no effect when the flexbox has only a single line.
Values: flex-start | flex-end | center | space-between | space-around | stretch Default: stretch
http://w3.org/tr/css3-flexbox/#align-content-property
@mixin align-content($value: stretch) {
// No Webkit Box Fallback.
-webkit-align-content: $value;
-moz-align-content: $value;
@if $value == flex-start {
-ms-flex-line-pack: start;
} @else if $value == flex-end {
-ms-flex-line-pack: end;
} @else {
-ms-flex-line-pack: $value;
}
align-content: $value;
}